Doctors are sometimes called as “mechanics of human bodies”. This term describes well current approach the science has regarding human body. In the past it was covered with a mystery of not well understood performance filled according to the humorism theory with 4 fluids: such as blood, yellow bile, phlegm and “black bile”, now our bodies are treated by physicians as object without secrets or as a complex, but fixable machinery. Latest technological advances are clear proof of that, especially regarding recent projects on human nervous system. Current medical achievements in that field provide surprisingly good results of merging electronic solutions with human tissue, suggesting that new reality in form of Cyberpunk 2077 world could be more real than someone expects. #prothesis #cybepunk #brain #thoughts
Spinal cord therapy
Let’s start from one of the main challenges in neural disorders – disconnection of spinal cord. It is a cause of paralysis – damaged spinal cord is not capable of transmitting nervous signal between the brain and rest of the body. There are attempts to regenerate the its connectivity with stem cells (1), and some of such therapies are already approved for test and further development by some countries like Japan (2). However, challenge is to have reliable and working solutions. Research with stem cells is far from that stage now. Thus, there is still a need for solution that could help patient get their physical performance back.
Prosthesis – bypassing spinal cord
Example of the interesting breakthroughs in the area of prostethic medicine took place in 2014, when scientists from Ohio helped paralyzed man (with damaged cord spinal) to move his hand with a thought. Surgeons had implanted a small array of electrodes in patient’s motor cortex to transmit his thoughts directly to his hand muscles and bypass his spinal injury. After many exhaustive trainings in the lab patient was able to pick up a bottle and pour water to a glass or play the guitar only by thoughts. All of these were possible with the specific computer system and technology to omit the spinal cord while transmitting signal from brain to the limb (3).
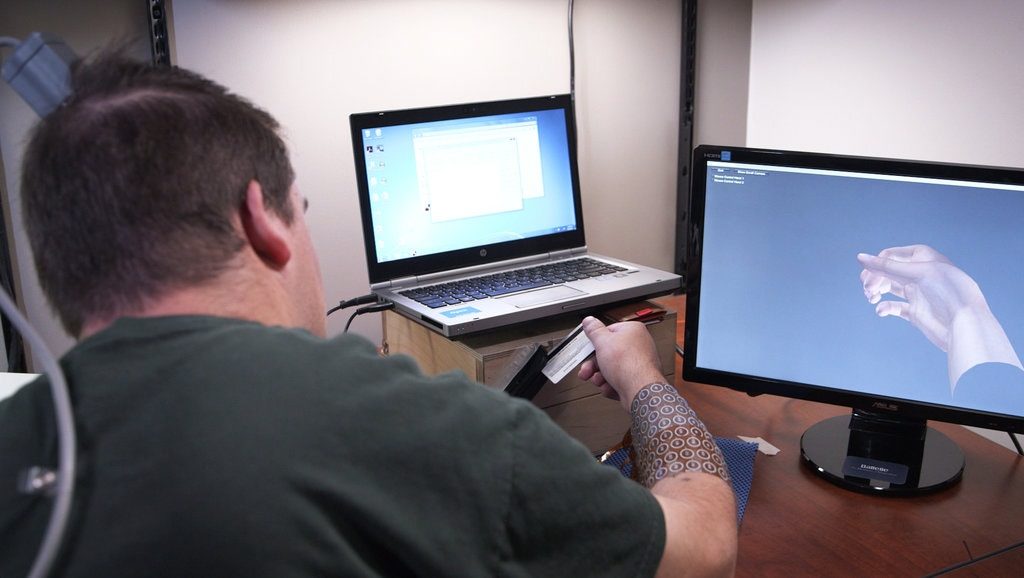

Connecting to the limb’s nervous system
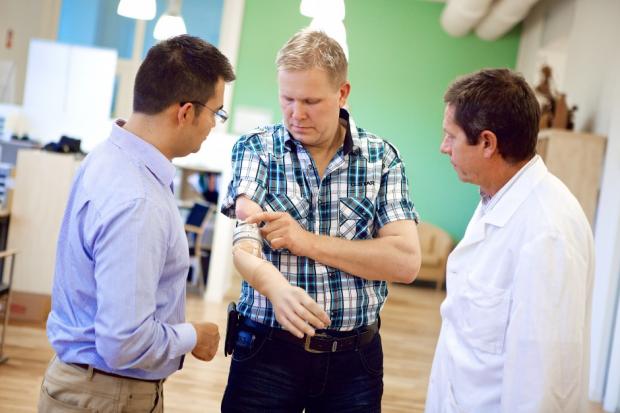
Different approach took scientists from Chalmers University in Sweden. They have developed an arm prosthesis that makes its users fit the definition of a cyborg, because it is connected directly to the bone, nerves and muscles of the patient. Solution uses sensors placed on the skin, while the central control system connects to nerve endings and muscles. Such prosthesis enables user more natural control of the arm, while it allows to feel what the hand is doing. Information about the movement and feelings goes both ways: through the wires to and from the arm, and the patient gets interactive feelings from various pressure points (4).

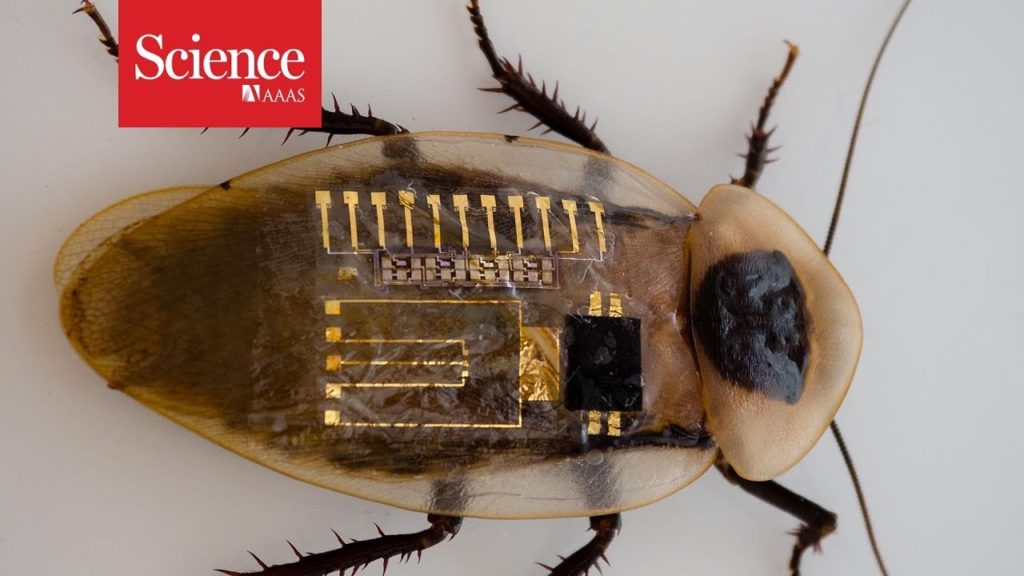
In last year, we have witnessed another interesting breakthrough that could help development of reliable and natural in performance prosthesis. Researchers from Cornell University have created a new type of artificial nerve that can sense touch, process information, and communicate with other nerves much like real ones. This device is made of three flexible organic components. First, a series of dozens of sensors to pick up pressure senses. Pressing on one of these sensors causes an increase in voltage between two electrodes. This change is then picked up by a second device called a ring oscillator, which converts voltage changes into a string of electrical pulses. These pulses, and those from other pressure sensor/ring oscillator combos, are fed into a third device called a synaptic transistor, which sends out a series of electrical pulses in patterns that match those produced by biological neurons. So far, the researchers detached a leg from a cockroach and inserted an electrode from the artificial neuron to a neuron in the cockroach leg, and signals coming from the artificial neuron caused muscles in the leg to contract. This is just beginning, but once developed technology could help construction of more complex and robust sensing devices capable of tracking changes in texture, position, and different types of pressure. New design of connections with human nervous system could even provide significant improvements in how people with artificial limbs (cyborgs) or robots can interact with its surroundings comparing to the natural systems.
Thus, this technology could go beyond current body limitations and help construction of more complex and robust sensing devices capable of tracking changes in texture, position, and different types of pressure. In effect, it could provide even significant improvements in how people with artificial limbs (cyborgs) or robots can interact with its surroundings (5).

Another noteworthy study was done by Graczyk et al., who have developed and tested with patients prosthesis enabling its sensation. However, comparing to the other scientists, this group has deeply validated expectations and feelings of the patients. Their sensory restoration system was based on tactile and proprioceptive sensations on the hand via neural stimulation through chronically implanted electrodes. In effect, patients loved much these devices, and some onf them were reluctant to take it off. “That’s because I like the sensation of having my hand there, and feeling like my hand was there, so I didn’t want to take it off” – one of them said. Scientists did a deep survey on the quality of life with new prosthesis among the study participants. In effect, the sensory feedback fundamentally altered the way participants used their prosthesis, transforming it from a sporadically used tool into a readily and frequently used hand. This is one of the most important features the new prosthesis solution would require to be successful on the market. Not only correctly transmit signal from brain to the device, but, if necessary, transmit it back and create information loop-back enabling illusion of having real limb attached to the body together with positive client’s experience (6).
Reading brain signals
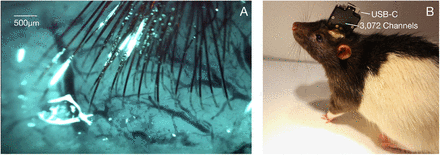
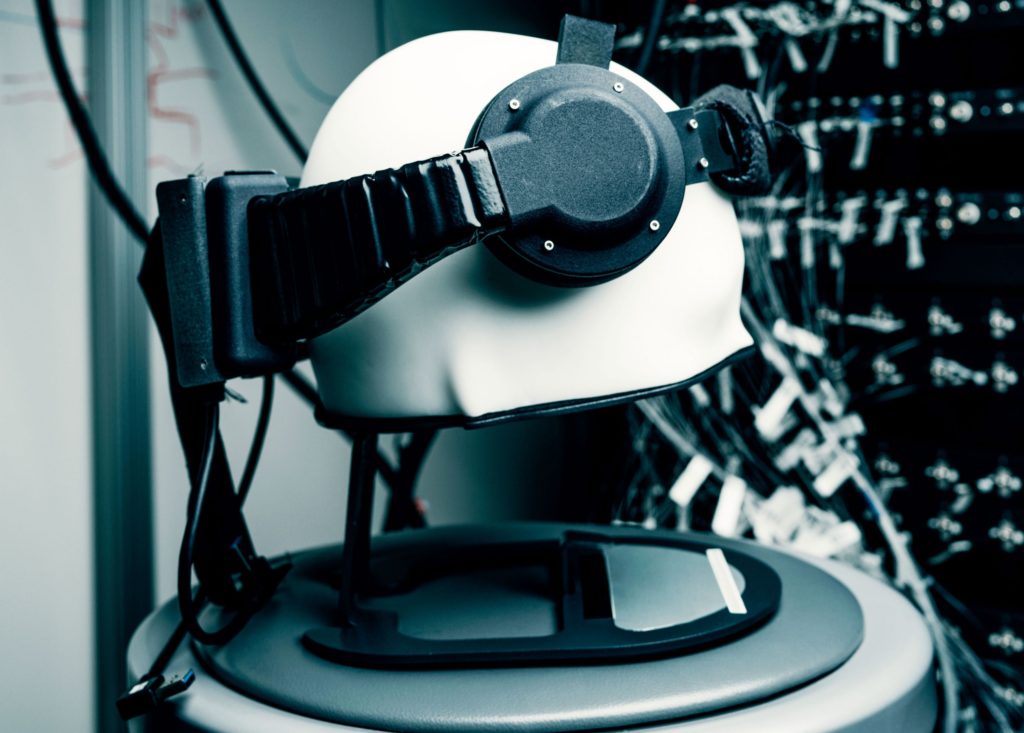
Elon Musk’s team works on the brain – machine interface for at least 2 years. Authors have built arrays of small and flexible electrode “threads”. Together with neurosurgical robot capable of inserting threads into the brain with micron precision and target specific brain regions. The electrode array is packaged into a small implantable device that contains custom chips for low-power on-board amplification and digitization. This system is promised to hold the necessary communication between the brain and the prosthesis or equipment. It is one of the most straightforward and potentially successful solutions in this area. Sewn in electrodes would set stable connection of the brain with external systems. Moroever, electrodes placement within structures of a brain could enable for stimulation of these areas and potentialy support therapy of damaged areas (7).
Other scientists has chosen a more ambitious path toward contact less reading human thoughts. Shinji Nishimoto and his team provided so far very promising tool for reading others’ minds (8). Solution utilizes the blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signals in brain that are measured via fMRI. As a basis for brain performance analysis, BOLD signals were perceived as not well accurate to formulate someone’s thought. However, current results are surprising and promise a significant breakthrough. Nishimoto team has asked group of volunteers to watch few movies, and measured brain blood activity during that time. Signals were mapped on human brain and analyzed with regard to the watched content. Trained software solution has enabled in backward reconstruction of some of the data basing on the measured signals. As you can see in the image below, there is an original image and reconstructed from signal measurements. Accuracy is not 100% perfect, but good enough to see the content and recognize it.

Analysis of the brain signals into the images and video by Shinji Nishimoto et al.
Almost at the same time Facebook has started research on reading our minds. Company wants to create a wearable headset that let users control music or interact in virtual reality using their thoughts. The work utilizes previously described monitoring the blood flow with an MRI machine. Despite of the fact, that such blood-flow patterns represent only a small part of what’s going on in the brain, they were also capable to read valuable information. The goal of Facebook research team is to enable users writing text only with a thought with a speed upto 100 words a minute. Moreover, such solution could enable expression and activation various commands, and this feature would bring the thought control systems and the next level of operating with machines – completely new world of technical possibilities. Facebook has plans to demonstrate a prototype of its portable system by the end of the year.

Wearable devices start to deeply penetrate our lives https://www.kgrzybowski.com/blog/wearable-for-insurance-purposes/
Pragmatic and demistyfied approach to treat human body as complex mechanism and apply technical rules and practices to combine its operations with external devices will bring soon very interesting and life changing solutions. Some of the researchers had assumed very “conservative” approach in binding human brain with a device by implementing chips directly to the brain. However, only in the case of prostehsis connection to the limb’s nerves this solution can be efficient and widely accepted by the users. Inconvenience of deep surgical operations for some of the developed devices could hamper their commercialization. End users would expect smooth and hassle free connection of artificial limb with body. In fact, Cyberpunk reality with cyborgs could be a reality shortly.
To avoid problem of deep integrations, some researchers took a step further and concentrated their efforts on reading human thoughts and converting them to the information. Current results are very promising and suggest a disruptive solutions. This would change our life in controlling and steering the neighborhood and the way we interact with environment. Considering both approaches for human integration with external devices it is probably a good time to ask for implications of prognosed developments. What would be the price people have to pay for their devotion to new technology? Will we sacrifice our current lifestyle or privacy?
(1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5979319
(2) (https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-019-00178-x
(3) https://www.nytimes.com/2016/04/14/health/paralysis-limb-reanimation-brain-chip.html
(4) http://sciencenordic.com/brain-controlled-prosthetic-arm-connected-nerves
(5) https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2018/05/new-artificial-nerves-could-transform-prosthetics
(6) https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-26952-x
(7) https://www.neuralink.com
(8) Shinji Nishimoto et al. Current Biology in 2011 (“Reconstructing Visual Experiences from Brain Activity Evoked by Natural Movies”), link: https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(11)00937-7